АКТУАЛЬНОСТЬ ИНФЕКЦИЙ ЖЕЛУДОЧНО-КИШЕЧНОГО ТРАКТА В СОВРЕМЕННОЙ КЛИНИЧЕСКОЙ ПРАКТИКЕ
Инфекции желудочно-кишечного тракта (ЖКТ) остаются одной из значимых проблем в современной клинической практике из-за высокой распространенности, разнообразия возбудителей и серьезных последствий для здоровья населения. В последние годы наблюдается изменение этиологической структуры острых кишечных инфекций (ОКИ): если ранее в ней преобладали бактериальные патогены, то теперь лидируют вирусные агенты, такие как ротавирусы и норовирусы [1, 2].
Согласно государственному докладу «О состоянии санитарно-эпидемиологического благополучия населения в Российской Федерации в 2023 году», в 2023 г. в России были зарегистрированы 269 очагов групповой заболеваемости норовирусной инфекцией с общим количеством пострадавших 3957 человек, что превысило показатели 2021 г. (210 очагов и 2882 пострадавших) [2].
Пандемия COVID-19 также внесла изменения в эпидемиологию инфекций ЖКТ. В 2020 и 2021 гг. наблюдалось снижение заболеваемости ОКИ, вероятно, связанное с введением ограничительных мероприятий – социального дистанцирования, гигиенических мер и снижения миграционной активности населения. Однако уже в 2021 г. наметилась тенденция к увеличению заболеваемости ОКИ неустановленной и установленной этиологии на 17,1 и 27,9% соответственно по сравнению с предыдущим годом. Эти данные подчеркивают необходимость постоянного мониторинга и адаптации клинических подходов к инфекционным патологиям ЖКТ в изменяющихся эпидемиологических условиях [2].
Параллельно с инфекционной патологией ЖКТ актуальной остается проблема функциональных расстройств пищеварительного тракта, которые отличаются хроническим течением и значительно влияют на качество жизни пациентов. Частота встречаемости таких состояний, как синдром раздраженного кишечника (СРК) и функциональная диспепсия, достигает 10–20% и выше в различных популяциях, причем у существенной доли пациентов выявляется сочетание нескольких функциональных нарушений, что еще более усложняет диагностику и терапию. Многие из этих состояний берут начало в детском возрасте и могут сохраняться во взрослой жизни; это подчеркивает важность ранней диагностики и комплексного патогенетически ориентированного подхода к их лечению [3–5].
Таким образом, актуальность инфекций ЖКТ в современной клинической практике обусловлена их высокой распространенностью, изменяющейся этиологической структурой [1], воздействием глобальных факторов, таких как пандемия COVID-19 [2], и значительным влиянием на качество жизни пациентов [3, 4].
ПРОБЛЕМА АНТИБИОТИКОРЕЗИСТЕНТНОСТИ И РОЛЬ БЕЗОПАСНЫХ АНТИБАКТЕРИАЛЬНЫХ ПРЕПАРАТОВ
Проблема антибиотикорезистентности представляет собой серьезную глобальную угрозу для здравоохранения, особенно актуальную при лечении инфекций ЖКТ. Чрезмерное и нерациональное применение антибиотиков приводит к появлению устойчивых штаммов микроорганизмов, затрудняя терапию инфекционных заболеваний. Поэтому особое внимание уделяется антибактериальным препаратам, которым свойственны минимальный риск развития устойчивости патогенов и благоприятный профиль безопасности [4, 6, 7].
Одним из таких препаратов является рифаксимин – невсасывающийся антибиотик широкого спектра действия, который успешно используется при синдроме избыточного бактериального роста (СИБР), диарее путешественников и печеночной энцефалопатии (ПЭ) [8–11]. Вследствие низкой системной абсорбции и высокой концентрации в просвете кишечника рифаксимин обеспечивает локальный антибактериальный эффект с минимальным воздействием на системный микробиом [8, 11].
Ранее считалось, что рифаксимин характеризуется низким риском развития антибиотикорезистентности, но последние исследования показывают более сложную ситуацию [6, 11]. В условиях растущей антибиотикорезистентности рифаксимин остается важным средством лечения инфекций ЖКТ ввиду локального действия и безопасности [8, 11]. Однако современные данные о возможной перекрестной резистентности говорят о необходимости осторожного и рационального использования этого препарата [2, 7, 10]. Врачам следует тщательно подходить к назначению рифаксимина, учитывать потенциальные риски и регулярно обновлять знания согласно последним клиническим рекомендациям [12].
ИСТОРИЯ СОЗДАНИЯ РИФАКСИМИНА
Рифаксимин – полусинтетический антибиотик из группы рифамицинов, разработанный в начале 1980-х гг. итальянской компанией Alfasigma (ранее – Alfa Wassermann). При его разработке целью было получение эффективного антибактериального препарата, имеющего минимальную системную абсорбцию, что позволяло бы воздействовать непосредственно на патогены в ЖКТ с наименьшим числом побочных эффектов [8, 11, 13].
В 1987 г. рифаксимин был впервые одобрен для медицинского применения в Италии. Ранние клинические исследования подтвердили его эффективность в лечении различных кишечных инфекций, включая диарею путешественников [8, 9, 14]. В частности, было показано, что препарат эффективен против энтерогеморрагической Escherichia coli, подавляя продукцию и высвобождение шигатоксина – основного фактора вирулентности этого патогена [8, 11].
Благодаря положительным результатам клинических испытаний и хорошей переносимости рифаксимин получил признание в медицинском сообществе и был одобрен для лечения различных заболеваний ЖКТ более чем в 30 странах [8, 11, 13]. Низкая системная абсорбция и широкий спектр антибактериальной активности сделали его ценным инструментом в терапии инфекций ЖКТ [8, 9, 11].
Рифаксимин прошел несколько ключевых этапов регистрации и внедрения в клиническую практику:
- 1987 г.: первое одобрение рифаксимина для медицинского применения в Италии [8];
- 2004 г.: Управление по санитарному надзору за качеством пищевых продуктов и медикаментов США (Food and Drug Administration, FDA) одобрило препарат под торговым названием Xifaxan в дозировке 200 мг для лечения диареи путешественников, вызванной неинвазивными штаммами E. coli [8, 14];
- 2010 г.: FDA одобрило Xifaxan 550 мг для снижения риска рецидива ПЭ у пациентов с хроническими заболеваниями печени [10];
- 2015 г.: Xifaxan 550 мг одобрен FDA для лечения СРК с диареей (СРК-Д) у взрослых [9, 12].
В Европе рифаксимин также получил признание: в гайдлайнах Европейской ассоциации по изучению печени (European Association for the Study of the Liver) рекомендуется применять рифаксимин в сочетании с лактулозой для вторичной профилактики рецидивов ПЭ [12].
Все это подчеркивает значимость рифаксимина в лечении различных желудочно-кишечных заболеваний и его широкое использование в клинической практике на международном уровне [8, 10, 12].
Важно отметить при этом, что все ключевые рандомизированные контролируемые исследования (РКИ) и метаанализы, на которых основаны современные рекомендации, проводились с применением оригинальной полиморфной формы рифаксимина α (в России он зарегистрирован под торговым наименованием Альфа Нормикс®). Она обеспечивает минимальную системную абсорбцию и стабильную локальную активность активного вещества в просвете кишечника. Препараты, содержащие другие полиморфные формы (β, γ и др.), не проходили сопоставимых исследований, и данные об их клинической эквивалентности отсутствуют. Поэтому при назначении рифаксимина в терапевтических целях предпочтение должно отдаваться оригинальной форме α, прошедшей полное доклиническое и клиническое изучение и исследования.
ОСНОВНЫЕ ФАРМАКОЛОГИЧЕСКИЕ СВОЙСТВА РИФАКСИМИНА
Фармакокинетика
- Абсорбция: после перорального приема рифаксимин в полиморфной форме α практически не всасывается в системный кровоток, что определяет его локальное действие в просвете кишечника. Менее 1% принятой дозы обнаруживается в плазме крови, что минимизирует риск системных нежелательных явлений [8, 11, 13].
- Распределение: благодаря низкой абсорбции рифаксимин достигает высоких концентраций в кишечнике, обеспечивая эффективное подавление патогенной микрофлоры. Исследования на животных продемонстрировали, что 80–90% принятой дозы препарата концентрируется в ЖКТ [8, 11].
- Метаболизм: небольшая часть абсорбированного рифаксимина метаболизируется в печени, главным образом с участием изофермента CYP3A4. Однако из-за крайне низкой системной абсорбции этот процесс не имеет клинически значимого влияния [8, 11].
- Выведение: основная часть препарата (> 96%) выводится с калом в неизмененном виде, что подтверждает его минимальную системную абсорбцию и локальное действие в кишечнике [8, 11, 13].
Фармакодинамика
Рифаксимин оказывает бактерицидное действие, необратимо связываясь с β-субъединицей бактериальной ДНК-зависимой РНК-полимеразы, что приводит к ингибированию синтеза РНК и подавлению роста и размножения широко спектра чувствительных к нему микроорганизмов, ассоциированных с инфекциями ЖКТ [6, 8, 11].
Помимо прямого антибактериального эффекта, рифаксимин обладает дополнительными свойствами:
- модуляцией микробиоты кишечника: препарат способствует нормализации состава кишечной микрофлоры, снижая количество патогенных бактерий и увеличивая долю полезных микроорганизмов. Это особенно важно при лечении СРК-Д и ПЭ [9–11, 14];
- противовоспалительным действием: рифаксимин может уменьшать воспаление в кишечнике путем снижения продукции провоспалительных цитокинов и укрепления барьерной функции кишечного эпителия [11, 14].
Таким образом, уникальные фармакокинетические свойства рифаксимина обеспечивают его локальное действие в кишечнике с минимальным системным воздействием [8, 11, 13], а его фармакодинамические эффекты делают его эффективным средством для лечения различных заболеваний ЖКТ [9, 10, 12].
Спектр антибактериальной активности рифаксимина включает:
- грамположительные аэробные бактерии: Staphylococcus aureus (в том числе метициллин-резистентные штаммы), Streptococcus pyogenes, Enterococcus faecalis, Enterococcus faecium, Bacillus cereus;
- грамположительные анаэробные бактерии: C. difficile, Clostridium spp., Peptococcus spp., Peptostreptococcus spp.;
- грамотрицательные аэробные бактерии: E. coli (энтеротоксигенные и энтероагрегативные штаммы), Salmonella spp., Shigella spp., Yersinia enterocolitica, Proteus spp., Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Vibrio cholerae;
- грамотрицательные анаэробные бактерии: Bacteroides fragilis, Bacteroides spp.;
- микроаэрофилы: Campylobacter jejuni, Helicobacter pylori.
Подчеркнем еще раз, что, несмотря на широкий спектр антибактериального действия, рифаксимин реализует эффект главным образом в полости кишечника благодаря крайне низкой степени всасывания в системный кровоток [8, 11]. Это обеспечивает высокие концентрации препарата в ЖКТ, эффективные против большинства энтеропатогенов [8, 9, 11].
Вместе с тем недавние исследования выявили потенциальные риски, связанные с длительным применением рифаксимина. В частности, было обнаружено, что его прием может способствовать развитию устойчивости к даптомицину – одному из немногих эффективных препаратов против ванкомицин-резистентного энтерококка (VRE). Это открытие вызывает обеспокоенность, поскольку даптомицин часто используется в качестве «последней линии» защиты против некоторых устойчивых инфекций [6, 7, 10].
Подводя итог, отметим, что рифаксимин за счет широкого спектра антибактериальной активности и локального действия в кишечнике является высокоэффективным средством для лечения различных желудочно-кишечных инфекций [8–10]. Тем не менее его назначение должно быть строго обоснованным с учетом текущих рекомендаций и возможных последствий продолжительного использования, включая потенциал развития перекрестной антибиотикорезистентности [6, 7, 12].
Преимущества перед другими антибиотиками
Рифаксимин обладает рядом преимуществ перед другими антибактериальными препаратами, особенно важным в контексте лечения заболеваний ЖКТ.
1. Отсутствие системного действия: рифаксимин в полиморфной форме α практически не всасывается из ЖКТ при пероральном приеме, что обеспечивает его локальное действие в кишечнике. Менее 1% принятой дозы лекарственного средства попадает в системный кровоток, благодаря чему достигаются его высокие концентрации непосредственно в просвете кишечника, что, в свою очередь, минимизирует риск системных побочных эффектов и лекарственных взаимодействий [8, 11, 13].
2. Влияние на микробиом кишечника: в отличие от большинства системных антибиотиков, способных значительно нарушать баланс кишечной микрофлоры, рифаксимин оказывает минимальное влияние на общий состав микробиома. Более того, согласно исследованиям, он способствует увеличению численности полезных бактерий, таких как Lactobacillus, при сохранении общей структуры микробиоты [11, 14]. Наряду с этим рифаксимин обладает противовоспалительными свойствами и может модулировать вирулентность патогенных микроорганизмов, снижая их способность к адгезии и транслокации через кишечный эпителий [11, 14].
Рифаксимин обеспечивает эффективное лечение инфекций и функциональных расстройств ЖКТ, минимизируя риски, связанные с системным воздействием и дисбиозом, что делает его предпочтительным выбором в сравнении с другими антибиотиками для терапии заболеваний кишечника [8, 9, 11, 14].
ПОКАЗАНИЯ К ПРИМЕНЕНИЮ
Рифаксимин применяется для лечения и профилактики ряда заболеваний ЖКТ. Ниже представлены основные показания, отраженные в инструкциях по медицинскому применению зарегистрированных форм препарата в России [15–17], а также направления активного использования рифаксимина в клинической практике на основании данных исследований последних лет (табл.) [3, 11, 13].
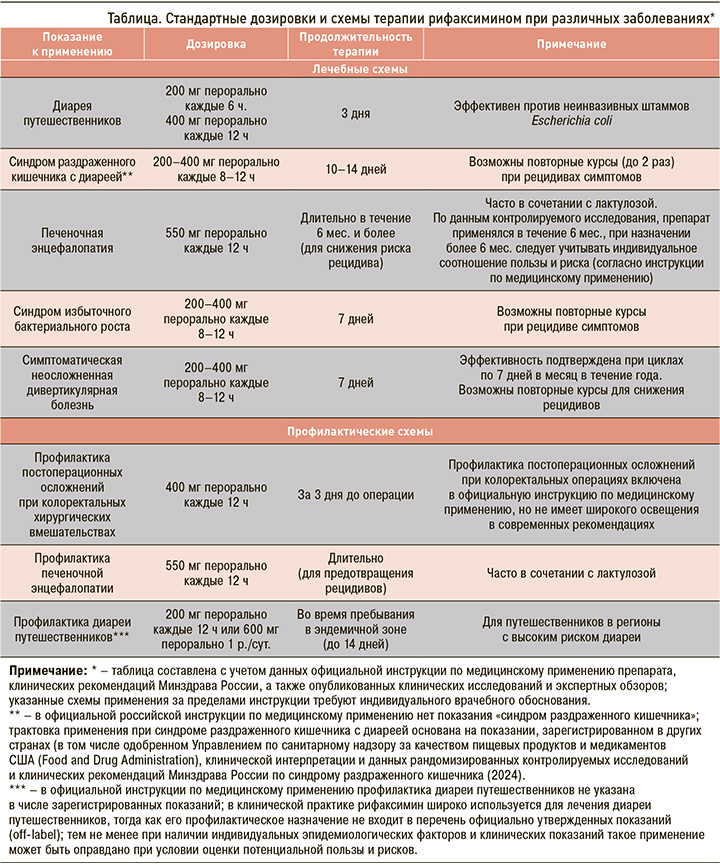
ОКИ и диарея путешественников
Рифаксимин эффективен при лечении ОКИ, возбудителями которых являются чувствительные к нему микроорганизмы [1]. Исследования подтверждают его эффективность и в терапии диареи путешественников, вызванной энтеротоксигенными и энтероагрегативными штаммами E. coli [8, 9, 14].
СИБР
СИБР характеризуется избыточным ростом бактерий в тонкой кишке, приводящим к таким симптомам, как вздутие, диарея и боль в животе [3, 14, 18]. Рифаксимин доказал свою эффективность при этом синдроме, способствуя улучшению состояния пациентов [9, 18]. По данным систематического обзора и метаанализа, препарат обладает дозозависимой эффективностью в терапии СИБР, уменьшая его желудочно-кишечные симптомы, при хороших показателях безопасности [6, 18, 19].
ПЭ
ПЭ – одно из наиболее значимых неврологических осложнений, возникающих на фоне тяжелых заболеваний печени, в частности цирроза [12]. Рифаксимин занимает прочное место в терапии ПЭ, применяясь как для купирования его клинических проявлений, так и с целью предотвращения рецидивов [12, 13, 15–17]. В клинических исследованиях прием рифаксимина способствовал снижению частоты эпизодов ПЭ, уменьшению потребности в госпитализации и улучшению когнитивных функций у пациентов с хроническими заболеваниями печени [10, 13, 20]. Кроме того, в соответствии с результатами систематического обзора Кокрановского сотрудничества препарат может положительно влиять на качество жизни больных с минимальной формой ПЭ [21].
Симптоматическая неосложненная дивертикулярная болезнь (СНДБ)
СНДБ – состояние, при котором на фоне наличия дивертикулов в толстой кишке развиваются такие хронические жалобы, как боль в животе, метеоризм и нестабильный стул, при отсутствии признаков выраженного воспаления. В патогенезе СНДБ важную роль играют локальные нарушения микробиоты и субклиническое воспаление, что объясняет обоснованность назначения рифаксимина [11, 22].
За счет способности снижать бактериальную нагрузку и уменьшать проявления микровоспаления рифаксимин используется как для купирования симптомов СНДБ в острый период, так и в виде профилактических курсов. Циклическое применение препарата (например, по 7–10 дней в месяц) позволяет достичь стойкого клинического улучшения и снизить частоту обострений [23]. Эффективность такой терапии подтверждена данными клинических исследований и отражена в официальных инструкциях к препарату [15–17].
Профилактика постоперационных осложнений при колоректальных хирургических вмешательствах
Рифаксимин может назначаться в предоперационном периоде коротким курсом с целью уменьшения бактериальной обсемененности кишечника и уменьшения риска послеоперационных осложнений, таких как инфекции операционного шва и внутрибрюшные инфекции [11, 15–17].
Несмотря на то что это показание официально включено в инструкции к нескольким формам препарата, в реальной клинической практике в России и за рубежом такой подход применяется ограниченно. Он редко упоминается в актуальных клинических рекомендациях, что подчеркивает необходимость дальнейших исследований и пересмотра места препарата в схемах предоперационной подготовки.
Хронические воспалительные заболевания кишечника (ВЗК)
Формулировка «хроническое воспаление кишечника» включена в инструкции к рифаксимину, однако без конкретизации нозологических форм [15–17]. В клинической практике под этим чаще всего понимаются легкие и умеренные формы ВЗК, включая болезнь Крона и язвенный колит, особенно в фазе ремиссии или при сопутствующем СИБР [22].
Рифаксимин оказывает локальное противомикробное и противовоспалительное действие, способен модулировать микробиоту и снижать продукцию провоспалительных цитокинов за счет активации PXR [11, 22].
Открытые исследования продемонстрировали, что прием рифаксимина может способствовать клиническому улучшению у пациентов с ВЗК, в том числе с болезнью Крона при длительном приеме в дозе 200 мг 3 раза в день [11, 16, 24, 25].
В клинических рекомендациях Минздрава России по язвенному колиту (2024) препарат рассматривается как возможный компонент терапии при легком течении заболевания, особенно в случае наличии признаков дисбиоза или СИБР [26]. Назначение рифаксимина в таких ситуациях требует индивидуального клинического обоснования.
При назначении рифаксимина важно соблюдать не только рекомендованную суточную дозу, но и равные интервалы между приемами, например, каждые 8 или 12 ч [15–17]. Нарушение временны́х промежутков может снижать эффективность терапии, особенно при длительном или повторном применении препарата. Пациенту необходимо разъяснять значимость строгого следования надлежащему режиму приема рифаксимина.
Продолжительность лечения и выбор схемы дозирования определяет врач с учетом клинической ситуации, переносимости препарата и динамики состояния пациента [15–17]. Назначение профилактических курсов требует обоснования индивидуальными факторами риска и должно проводиться под контролем врача.
ПРИМЕНЕНИЕ РИФАКСИМИНА В РЕАЛЬНОЙ КЛИНИЧЕСКОЙ ПРАКТИКЕ
Рифаксимин востребован в практике врачей различных специальностей, включая гастроэнтерологов, терапевтов, инфекционистов и хирургов. Препарат используется не только по перечню зарегистрированных показаний, но и в различных клинических ситуациях на основе накопленного опыта и данных современных исследований [11, 13, 15–17, 22, 23]. Это обусловлено его благоприятным профилем безопасности, хорошей переносимостью, выраженным клиническим эффектом и накопленным опытом применения. Ниже представлены примеры назначения рифаксимина в междисциплинарной клинической практике в соотнесении с показаниями официальной инструкции.
ОКИ и диарея путешественников
Рифаксимин зарегистрирован в России для лечения неосложненных форм диареи, вызванной неинвазивными штаммами E. coli, преимущественно энтеротоксигенными и энтероагрегативными. Эффективность препарата подтверждена в ряде РКИ: он достоверно сокращает продолжительность заболевания, уменьшает выраженность симптомов и нормализует частоту стула [8, 9, 14–17].
В клинической практике рифаксимин используется как у пациентов с острым эпизодом кишечной инфекции, так и у лиц, направляющихся в регионы с высоким риском диареи. При этом профилактическое применение препарата не отражено в официальных инструкциях по медицинскому применению и относится к стратегиям off-label, требующим индивидуального клинического обоснования.
СРК-Д
СРК-Д не входит в перечень зарегистрированных показаний рифаксимина в России. Тем не менее в международной клинической практике он активно применяется при этой форме функциональных расстройств кишечника. Его эффективность подтверждена в ряде РКИ и метаанализов: прием рифаксимина способствует уменьшению вздутия, нормализации частоты стула и общему улучшению самочувствия [6, 9, 27–29].
Считается, что терапевтический эффект рифаксимина связан с подавлением патобионтов и модуляцией кишечной микробиоты [11, 19, 22]. В нашей стране назначение рифаксимина при СРК-Д осуществляется off-label и требует индивидуального клинического обоснования [15–17]. В практике используют короткие курсы назначения препарата по 7–14 дней с возможностью повторного применения.
СИБР
СИБР включен в перечень показаний к применению рифаксимина, отраженный в официальной инструкции по медицинскому применению [15– 17]. Препарат оказывает локальное противомикробное действие [8, 11], способствуя эрадикации избыточной микрофлоры в тонкой кишке, что сопровождается уменьшением выраженности таких симптомов, как вздутие, диарея, боль в животе и нестабильный стул [14, 19, 22].
Доказательная база включает результаты систематических обзоров и метаанализов [6, 14, 19], подтверждающих эффективность и безопасность рифаксимина при терапии СИБР. В случае рецидива возможно проведение повторных курсов терапии под контролем врача [2, 5, 9, 14–17].
ПЭ
В перечень официальных показаний к применению рифаксимина, в том числе в форме 550 мг [15–17], входят лечение и профилактика ПЭ. Препарат используется как при клинически выраженной ПЭ, так и с целью предупреждения ее рецидивов [21, 22, 30].
Согласно данным клинических исследований и метаанализов, рифаксимин достоверно снижает риск развития и рецидивов ПЭ, не увеличивая частоту побочных эффектов, а также способствует улучшению когнитивных функций и снижению частоты госпитализаций у пациентов с циррозом печени (ЦП) [10, 13, 21]. Оптимальный эффект достигается при комбинации рифаксимина с лактулозой [10, 12, 13, 15, 30].
СНДБ
СНДБ также содержится в перечне официальных показаний к применению рифаксимина [15–17]. Препарат используется как для купирования проявлений этого заболевания, так и с профилактической целью [3, 15–17, 23]. В международной практике, особенно в Италии, рифаксимин широко применяется циклически – по 7–10 дней в месяц на протяжении нескольких месяцев [3, 11, 22]. Такой подход позволяет снизить частоту обострений и улучшить качество жизни пациентов [23].
Болезнь Крона и язвенный колит
Болезнь Крона и язвенный колит относятся к ВЗК, при которых рифаксимин может использоваться в составе комбинированной терапии у пациентов с легким и умеренным течением. Возможность применения препарата отражена в ряде клинических рекомендаций, включая рекомендации Минздрава России по язвенному колиту (2024), особенно при наличии признаков СИБР или дисбиоза [26]. Официальная инструкция к препарату в разделе «Показания» содержит в том числе хронические ВЗК. Механизм действия рифаксимина включает подавление патогенной микрофлоры, снижение воспаления и модуляцию микробиоты, что способствует уменьшению симптомов и улучшению качества жизни пациентов [11, 22, 25]. Отдельные открытые исследования продемонстрировали клиническое улучшение при применении рифаксимина в дозе 200 мг 3 раза в день на протяжении 12–16 нед. [24, 25]. Препарат хорошо переносится и может рассматриваться в качестве компонента поддерживающей терапии ВЗК, особенно при наличии признаков дисбиоза и СИБР [26].
Профилактика инфекционных осложнений при колоректальных хирургических вмешательствах
Эта область применения рифаксимина включена в перечень официальных показаний (официальные инструкции по медицинскому применению форм 200 и 400 мг) [15, 16]. Препарат в этом случае назначается коротким курсом до вмешательства с целью снижения бактериальной нагрузки в просвете кишечника и уменьшения риска послеоперационных инфекционных осложнений, включая раневые инфекции и инфекции брюшной полости [11, 15, 16].
ДОКАЗАТЕЛЬНАЯ БАЗА ЭФФЕКТИВНОСТИ ПРЕПАРАТА: ОБЗОР КРУПНЫХ ИССЛЕДОВАНИЙ И МЕТААНАЛИЗОВ
Эффективность применения рифаксимина подтверждена рядом крупных исследований и метаанализов, проведенных за последние 10 лет. Представляем обзор ключевых данных.
СРК
Метаанализы и систематические обзоры. В метаанализе, включавшем 6 РКИ, было показано, что рифаксимин эффективно уменьшает вздутие живота и обеспечивает общее облегчение симптомов у пациентов с СРК [6, 27, 28]. При этом не было выявлено существенных различий в частоте побочных эффектов между группой рифаксимина и плацебо [6, 27].
ПЭ
Клинические исследования. Рифаксимин продемонстрировал эффективность в профилактике рецидивов ПЭ у пациентов с ЦП [10, 12, 20, 21, 30]. В одном из исследований его применение приводило к снижению частоты рецидивов и улучшению качества жизни пациентов [10, 13, 21].
Помимо снижения частоты рецидивов ПЭ, прием рифаксимина у пациентов с ЦП может иметь дополнительные положительные эффекты. Так, при терапии ПЭ любой стадии у пациентов с компенсированным и декомпенсированным ЦП препарат назначается для снижения уровня аммиака в крови, улучшения психического статуса, уменьшения выраженности астериксиса, снижения стадии энцефалопатии. Использование рифаксимина у больных с рефрактерным асцитом продемонстрировало повышение 6-месячной выживаемости. Наряду со снижением риска инфицирования асцитической жидкости, у пациентов с ЦП на фоне терапии рифаксимином наблюдалось увеличение общей выживаемости, при этом частота развития C. difficile-ассоциированной диареи не превышала таковую для пациентов, получавших лактулозу. Применение рифаксимина сопровождается снижением риска осложнений ЦП и увеличением общей выживаемости у пациентов с ПЭ [31]. Назначение препарата при ЦП и ПЭ любой стадии включено в критерии оказания качества медицинской помощи [32].
Диарея путешественников
Клинические исследования. Рифаксимин эффективен в лечении диареи путешественников, вызванной чувствительными штаммами E. coli [8, 9, 15]. По данным исследований, его применение рифаксимина сокращает продолжительность и тяжесть симптомов этого заболевания [8, 9].
СИБР
Клинические исследования. Рифаксимин подтвердил эффективность в эрадикации СИБР и улучшении симптоматики (вздутие, диарея и боль в животе) [14–17, 19, 20].
Дивертикулярная болезнь
Метаанализы и систематические обзоры. В метаанализе Bianchi M. et al., включавшем исследования по длительной терапии неосложненной дивертикулярной болезни, было установлено, что циклическое применение рифаксимина по 7–10 дней ежемесячно в течение 12 мес. достоверно уменьшает частоту обострений заболевания и выраженность симптомов по сравнению с плацебо или отсутствием лечения. Авторы отметили хорошую переносимость препарата и отсутствие значимых побочных эффектов, что делает рифаксимин одним из предпочтительных средств у пациентов с рецидивирующим течением дивертикулярной болезни [33].
Клинические исследования. В российском неинтервенционном исследовании, проведенном среди пациентов с неосложненной симптоматически выраженной дивертикулярной болезнью, прием рифаксимина α (Альфа Нормикс®) привел к значительному уменьшению симптомов и достижению длительной ремиссии [23].
В 8-летнем ретроспективном исследовании Di Mario F. et al. было продемонстрировано, что регулярное циклическое применение рифаксимина у пациентов с СНДБ позволяет существенно снизить выраженность боли и вздутия живота, а также сократить частоту осложнений по сравнению с симптоматической терапией [34].
ВЗК
Клинические исследования. В исследованиях рифаксимин показал свой потенциал в лечении ВЗК, включая болезнь Крона и язвенный колит [22, 24–26]. Использование препарата вызывало клиническое улучшение и уменьшение воспаления у пациентов с этими заболеваниями.
Применение у детей
Рифаксимин применяется в педиатрической практике при острых и хронических кишечных инфекциях, включая случаи диареи, обусловленной нарушением баланса микрофлоры, энтеропатогенными бактериями и СИБР. Согласно опубликованным данным, препарат разрешен к применению у детей старше 12 лет, а также использовался в ряде исследований у детей младшего возраста при инфекционных заболеваниях ЖКТ [28, 35].
Так, в клинических исследованиях было показано, что рифаксимин эффективен у детей с острыми диарейными синдромами: его прием сопровождался значительным сокращением продолжительности диареи, уменьшением выраженности симптомов и хорошей переносимостью [28, 35, 36].
Кроме того, в исследовании Scarpellini E. et al. (2013) терапия рифаксимином в дозе 600 мг/сут. в течение 7 дней у детей с СРК и подтвержденным СИБР привела к нормализации дыхательного теста у 64% пациентов и существенному снижению выраженности симптомов (боль в животе, вздутие и метеоризм) [37].
Таким образом, несмотря на то что часть исследований носили открытый или пилотный характер, накопленные данные подтверждают эффективность и безопасность применения рифаксимина у детей при функциональных и инфекционных заболеваниях ЖКТ.
В соответствии с клиническими рекомендациями у детей с СРК рифаксимин применяется в суточной дозе 600 мг, разделенной в 3 приема, курсом 7 дней (с 7 лет) [38].
Однако требуется проведение более масштабных РКИ для уточнения дозировок и схем лечения для детей младшего возраста.
Таким образом, доказательная база эффективности рифаксимина включает результаты многочисленных исследований и метаанализов, что обосновывает его широкое применение в клинической практике для лечения различных заболеваний ЖКТ.
ОПЫТ ИСПОЛЬЗОВАНИЯ РИФАКСИМИНА В РОССИИ
В России оригинальный рифаксимин официально зарегистрирован и представлен на фармацевтическом рынке под торговым названием Альфа Нормикс® [15–17]. Пострегистрационные многоцентровые исследования реальной клинической практики подтверждают его эффективность и безопасность при лечении различных патологии ЖКТ:
- дивертикулярная болезнь: в российском неинтервенционном исследовании оценивалась эффективность рифаксимина α у пациентов с СНДБ. Результаты показали значительное уменьшение симптомов и достижение длительной ремиссии [23];
- минимальная ПЭ (МПЭ): в многоцентровом исследовании NORMIND сравнивалась эффективность непрерывного и циклического применения рифаксимина α у пациентов с ЦП и МПЭ. Непрерывный режим терапии в течение 12 мес. показал более выраженное улучшение качества жизни и снижение симптомов МПЭ [39].
БЕЗОПАСНОСТЬ И ПЕРЕНОСИМОСТЬ
Рифаксимин обладает благоприятным профилем безопасности, что обусловлено его фармакокинетическими свойствами. Клинические исследования и метаанализы демонстрируют, что препарат хорошо переносится большинством пациентов, а частота нежелательных явлений при его применении сопоставима с таковой в группе плацебо [6, 9, 12, 13, 19, 21]. Многократные курсы лечения рифаксимином (например, при СРК или СИБР) также характеризуется высоким уровнем переносимости и отсутствием кумулятивных токсических эффектов. Согласно исследованиям, повторное назначение препарата не сопровождается возрастанием частоты побочных реакций [6, 9, 10, 13, 19].
В то же время в клинической практике необходимо учитывать определенные проблемы и ограничения при его применении, рассмотренные ниже.
Возможные побочные эффекты и безопасность препарата
К числу возможных нежелательных реакций рифаксимина относятся:
- cо стороны ЖКТ: тошнота, диспепсия, рвота, боли в животе, колики. Эти симптомы обычно проходят самостоятельно без необходимости отмены препарата [19, 28];
- аллергические реакции: редко наблюдаются крапивница, кожные высыпания [6];
- другие реакции: головная боль, головокружение, утомляемость, периферические отеки, мышечные спазмы [10, 11, 39].
При этом большинство побочных эффектов препарата являются легкими или умеренными и не требуют прекращения терапии [11, 22].
Риск развития антибиотикорезистентности и стратегии ее предупреждения
Для рифаксимина характерен низкий потенциал к развития бактериальной резистентности вследствие особенностей механизма его действия и минимального воздействия на комменсальную микрофлору [8, 11, 22]. Тем не менее длительное и неконтролируемое применение любого антибиотика может способствовать развитию устойчивых штаммов микроорганизмов [6, 7, 39]. Для минимизации этого риска следует:
- придерживаться рекомендованных схем дозирования и продолжительности терапии. Стандартная длительность лечения рифаксимином не должна превышать 7 дней, а повторные курсы проводятся не ранее чем через 20–40 дней [10, 12, 13, 19]. При ПЭ возможно применение препарата в течение 6 мес. В случае необходимости его приема свыше этого срока следует учитывать индивидуальное соотношение пользы и риска (согласно инструкции по медицинскому применению);
- избегать необоснованного назначения антибиотика. Рифаксимин необходимо использовать только при подтвержденных показаниях и под контролем врача [6, 7];
- проводить мониторинг клинической эффективности. При отсутствии положительной динамики следует пересмотреть диагноз и тактику лечения.
Ограничения к назначению (противопоказания)
Применение рифаксимина противопоказано или требует осторожности в следующих случаях:
- гиперчувствительность к этому лекарственному средству или другим антибиотикам группы рифамицинов. Аллергические реакции на эти препараты служат абсолютным противопоказанием к их назначению [11, 15–17];
- беременность и период лактации. Применение рифаксимина при беременности возможно только в случае крайней необходимости и под непосредственным наблюдением врача. На время лечения рекомендуется прекратить грудное вскармливание, поскольку неизвестно, проникает ли рифаксимин в грудное молоко [8, 11];
- детский возраст до 12 лет. Безопасность и эффективность рифаксимина у детей младше 12 лет не установлены, поэтому его применение в этой возрастной группе не рекомендуется [8, 11, 13, 15–17]. Однако в соответствии с действующими клиническими рекомендациями у детей с СРК допускается применение рифаксимина с 7 лет в дозе 600 мг/сут. в течение 7 дней [38]. В подобных случаях решение о назначении должно приниматься с учетом потенциальной пользы и индивидуального клинического состояния пациента.
В целом рифаксимин является эффективным и относительно безопасным препаратом для лечения ряда заболеваний ЖКТ [8, 9, 11]. Однако его применение должно быть обоснованным, с учетом возможных побочных эффектов и противопоказаний [6, 7, 13, 22, 39]. Следует учитывать, что при длительной терапии, например, у пациентов с ПЭ, риск развития резистентности остается низким по сравнению с другими антибиотиками за счет минимальной системной абсорбции препарата.
ЗНАЧЕНИЕ РИФАКСИМИНА В СОВРЕМЕННОЙ КЛИНИЧЕСКОЙ ФАРМАКОЛОГИИ И ТЕРАПИИ И ПЕРСПЕКТИВЫ ДАЛЬНЕЙШЕГО РАСШИРЕНИЯ ПОКАЗАНИЙ К ПРИМЕНЕНИЮ
Рифаксимин занимает важное место в современной клинической фармакологии благодаря высокой эффективности, локальному действию и благоприятному профилю безопасности при лечении различных заболеваний ЖКТ [6, 8–11, 13, 19, 28]. Это делает его препаратом выбора при лечении ОКИ, СИБР, ПЭ и диареи путешественников [1, 8–10, 14–17, 21].
Клинические исследования указывают на потенциал рифаксимина в модуляции кишечной микробиоты, что открывает перспективы для его использования при различных заболеваниях, связанных с дисбиозом кишечника [11, 14, 19, 22]. Современные данные свидетельствуют о возможностях комбинированного приема рифаксимина, в том числе в сочетании с пре- и пробиотиками, с целью усиления клинического эффекта, оптимального восстановления микробиоты кишечника и повышения качества жизни пациентов [6, 19, 22, 29].
Врачам различных специальностей важно учитывать индивидуальные особенности пациентов при назначении рифаксимина [12, 15–17, 26]. Следует строго соблюдать рекомендованные дозировки и продолжительность терапии, а также учитывать наличие возможных противопоказаний и индивидуальную переносимость препарата [10, 15–17]. В условиях растущей антибиотикорезистентности применение таких препаратов, как рифаксимин, требует рационального подхода, опирающегося на принципы доказательной медицины и клинические рекомендации [1, 6, 7, 11, 12, 26].



